Taking those first steps
Marketing is a dynamic field which requires creativity, strategy, and analytical skills. If you’re looking to start a career in marketing, understanding some of the core theories, models, and elements is essential.
Now, I’m not saying that understanding these things will make you a marketing wizard, or, that you’ll actually use all of them. However, having a good understanding of the foundational elements can be massively beneficial in the long run.
This article provides an overview of key concepts you should look to grasp in order to build a strong foundation in marketing. From fundamental theories like the Marketing Mix and SWOT Analysis to practical skills such as digital marketing and brand management, it’s important to try and get as many of these under your belt as possible.
Whether you’re preparing for your first marketing job or looking to refine your existing knowledge, these insights will help you navigate the evolving landscape of marketing with confidence.
Let’s get started.
Marketing theories and models

Marketing Mix (4 Ps and 7 Ps)
The Marketing Mix, comprising Product, Price, Place, and Promotion (4 Ps), is a foundational model for developing marketing strategies. It guides how to position a product in the market, determine pricing, choose distribution channels, and create promotional tactics, essential for effectively reaching and engaging customers.
- 4 Ps: Product, Price, Place, Promotion.
- 7 Ps: Extends the 4 Ps to include People, Process, and Physical evidence.

SWOT analysis
SWOT Analysis assesses the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of a business or project. It’s crucial to identify internal advantages and areas for improvement, as well as external factors to leverage or mitigate, guiding strategic planning and informed decision-making in marketing.
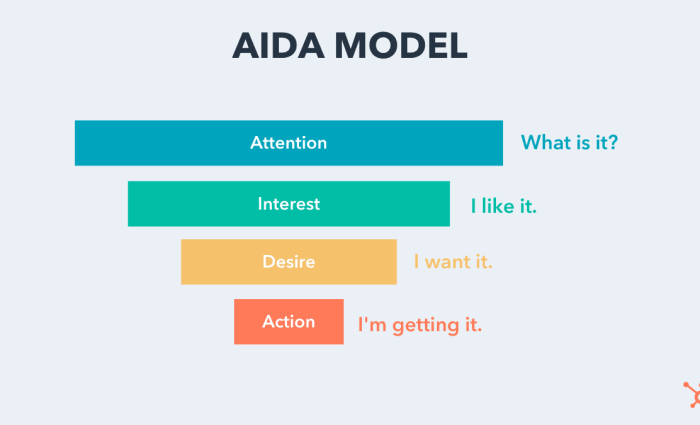
AIDA model
The AIDA model outlines the customer journey stages: Attention, Interest, Desire, and Action. It’s essential for crafting marketing messages that capture attention, generate interest, build desire, and drive actions, effectively converting prospects into customers.
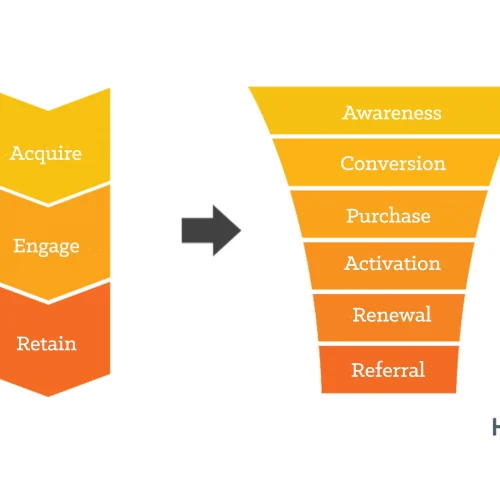
Customer Lifecycle
The Customer Lifecycle encompasses the stages a customer goes through Awareness, Consideration, Purchase, Retention, and Advocacy. Sometimes these names are interchangeable, however. It’s vital for understanding and optimising interactions at each phase. By tailoring strategies to each stage, businesses can effectively attract new customers, enhance their buying experience, maintain engagement, and turn satisfied customers into loyal advocates, thereby maximising long-term value and growth.
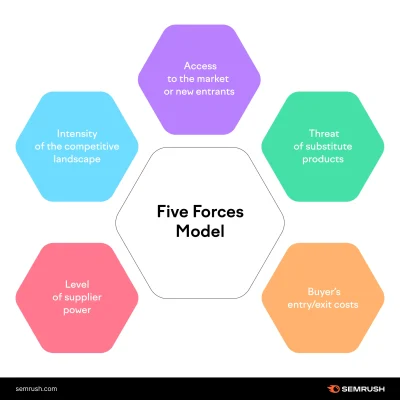
Porter’s Five Forces (intermediate)
Porter’s Five Forces analyses the competitive forces shaping an industry: Competitive Rivalry, Supplier Power, Buyer Power, Threat of New Entrants, and Threat of Substitutes. This model is crucial for understanding market dynamics and the intensity of competition. It helps identify opportunities and threats, assess industry attractiveness, and develop strategic positions to improve profitability and market standing. By evaluating these forces, marketers can make informed decisions about entering or competing within a market.
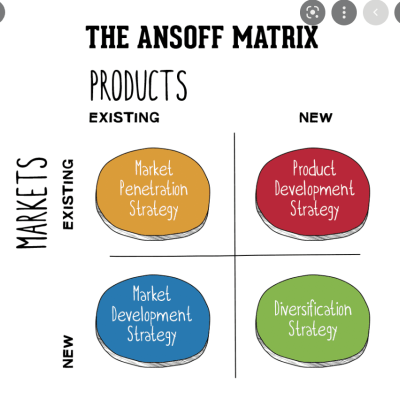
Ansoff Matrix (intermediate)
The Ansoff Matrix identifies growth strategies through four quadrants: Market Penetration (existing products, existing markets), Market Development (existing products, new markets), Product Development (new products, existing markets), and Diversification (new products, new markets). It’s essential for assessing risk and guiding strategic expansion decisions, helping businesses explore and implement growth opportunities effectively based on market and product dynamics.
Marketing concepts
Here is a list of some of the core concepts, terms, and elements of marketing it’s useful to understand before pursuing a career in marketing. Again, it’s not necessary for you to understand them in great depth to start with. However, having a foundational understanding of them will put you in a great position.
Market research
Market Research involves gathering data to understand market conditions and customer preferences. It includes Primary Research (direct data collection through surveys, interviews, and focus groups) and Secondary Research (analysis of existing data like reports and studies). It’s essential for making informed marketing decisions, identifying opportunities, understanding customer needs, and reducing business risks, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of marketing strategies.
Consumer behavior
Consumer Behavior studies how individuals or groups select, purchase, use, and dispose of products. Influenced by psychological (motivation, perception), social (family, culture), personal (age, lifestyle), and situational factors, it’s crucial for marketers to understand these behaviours to tailor their strategies effectively, meet customer needs, predict market trends, and create compelling marketing messages that resonate with target audiences.
Brand management
Brand Management involves overseeing and positioning a brand in the market to create a distinctive identity and achieve strategic goals. It encompasses Brand Identity (core values, mission), Brand Equity (perceived value and loyalty), Brand Positioning (differentiation from competitors), and Brand Loyalty (customer retention). Effective brand management ensures consistency across all touchpoints, builds strong emotional connections with consumers, and maximises brand value and market presence over time.
Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing leverages online channels to reach and engage target audiences. It includes various tactics such as Search Engine Optimization (SEO) to improve visibility on search engines, Social Media Marketing to interact with users on platforms like Facebook and Instagram, Email Marketing for direct communication, and Content Marketing through blogs, videos, and infographics.
Essential for today’s businesses, digital marketing allows precise targeting, real-time analytics, and cost-effective campaigns to drive conversions and brand awareness in the digital space.
Content marketing
Content Marketing involves creating and distributing valuable, relevant content to attract and engage a target audience. It aims to build trust, educate, and influence purchasing decisions without explicitly promoting a brand. Through blogs, videos, eBooks, and more, content marketing establishes authority, enhances SEO, and fosters long-term relationships with customers. It’s essential for driving organic traffic, increasing brand visibility, and nurturing leads into loyal customers.
Advertising and promotion
Advertising and Promotion are strategic communication tools used to promote products or services to target audiences.
Advertising includes traditional media (TV, radio, print) and digital channels (display ads, social media ads). Promotion involves sales promotions, public relations, and sponsorships to enhance brand visibility and stimulate sales. These activities aim to create brand awareness, influence consumer behaviour, and maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
Public Relations (PR)
Public Relations (PR) manages an organisation’s reputation through strategic communication with the public, media, and stakeholders. It involves activities such as media relations, crisis management, community engagement, and event coordination.
PR aims to build positive brand perception, handle crises effectively, and maintain goodwill. By fostering relationships and generating favourable publicity, PR enhances credibility, trust, and overall brand image in the eyes of the public.
Marketing Analytics
Marketing Analytics involves measuring, managing, and analysing marketing performance to optimise strategies and drive business growth. It includes tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), analysing customer behaviour, and assessing campaign effectiveness through data-driven insights.
Marketing analytics informs decision-making, improves ROI, and enables marketers to allocate resources effectively across various channels, ensuring continuous improvement and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Wrapping up
So, as mentioned at the start of this article, to excel in marketing you’ll need foundational knowledge of key theories and concepts to ensure your success. Understanding things like the Marketing Mix, SWOT Analysis, and other models can help aid you in crafting effective strategies and/or understanding what is happening within marketing campaigns.
Understanding concepts like consumer behaviour and brand management will provide you with insights into customer preferences and brand positioning. Additionally, proficiency in digital marketing, content creation, and PR enhances your ability to gain engagement and brand reputation. Understanding things like market research and analytics will help to ensure you make informed decisions.
Starting your mastery of these elements now will help you on your journey as a marketer and help you navigate the initial challenges when you enter the field. With all this said, if you’re looking to start a career in marketing, why not check out some of our apprenticeship vacancies and see whether a marketing apprenticeship could be an effective route into the field?
Interested in seeing more of our guides, advice, and articles on marketing apprenticeships?
Then sign up for our monthly newsletter. We’ll send you all the information on our latest stuff and general updates as well. Sign up below!